Testing the Search Widget
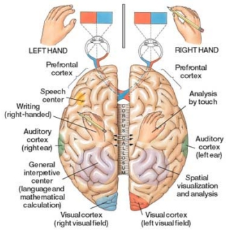
A reading text on the evolution of left-right handedness and the role of the brain
Teaching resources and information for learning about the concept of evolutionary mismatch in human behavior and its potential role in sustainable development
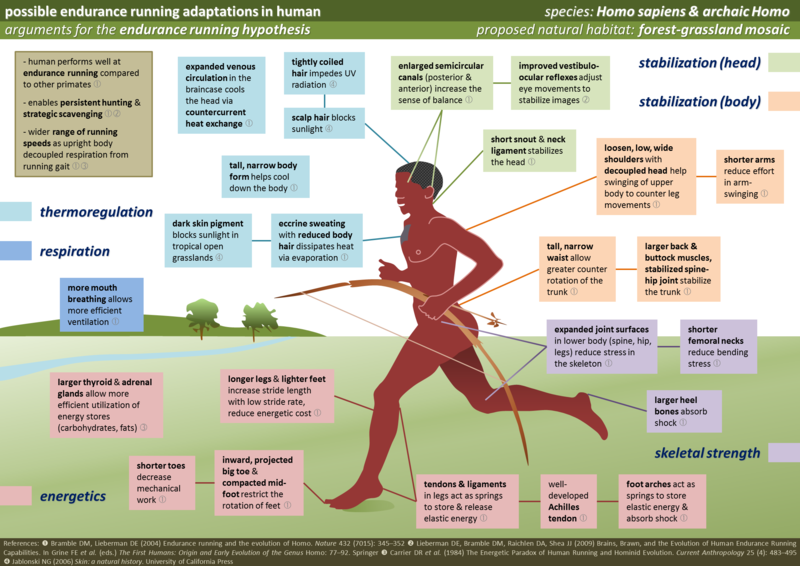
Reading texts, videos and causal maps on the evolution of physical and cognitive traits for endurance running over the course of human evolution
A lesson collection for learning about the origins, diversity, and flexibility of goal-directed behaviors.
This video is about domestication – or “taming by breeding” – of foxes, a Russian research project that has been conducted since the 1950s.
Scientific insight and video art through the Inspiration Journey project.
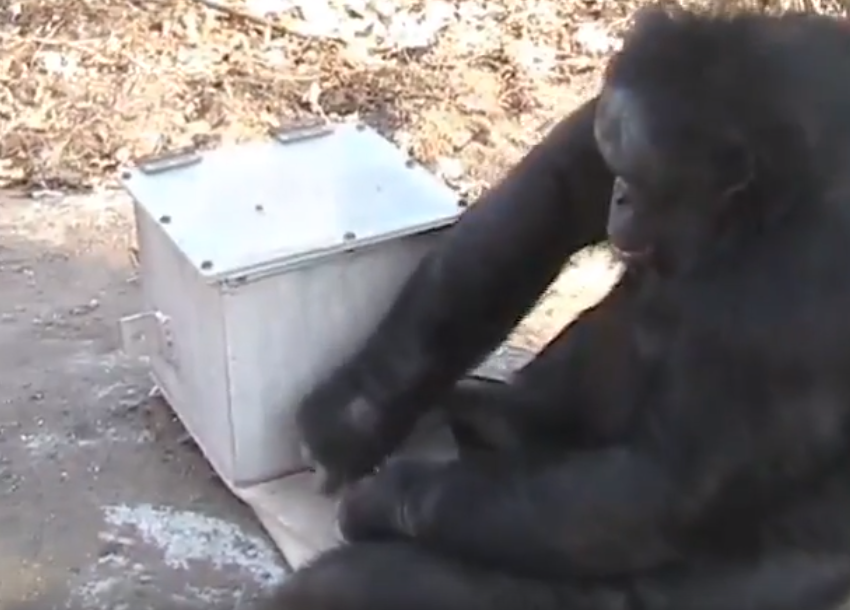
The bonobo Kanzi was taught to make and use simple stone tools of the Oldowan culture. What can we conclude about the mental abilities
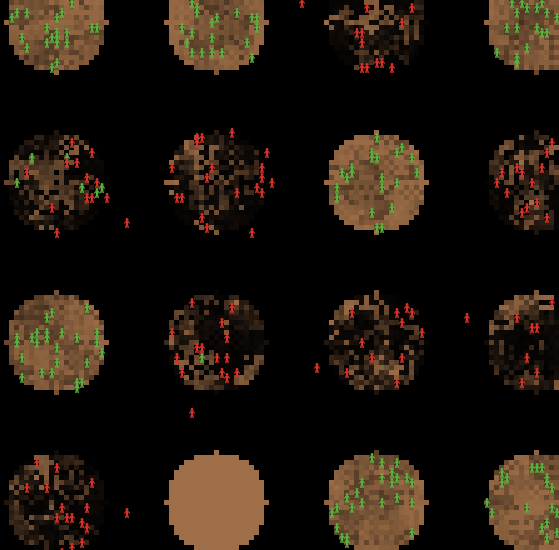
This model simulates the biological evolution of ethnocentrism in a population made up of multiple ethnicities.
A reading text about tool use and tool making in the animal kingdom and in our early ancestors
A lesson collection for the Human Behavior & Sustainable Development module.
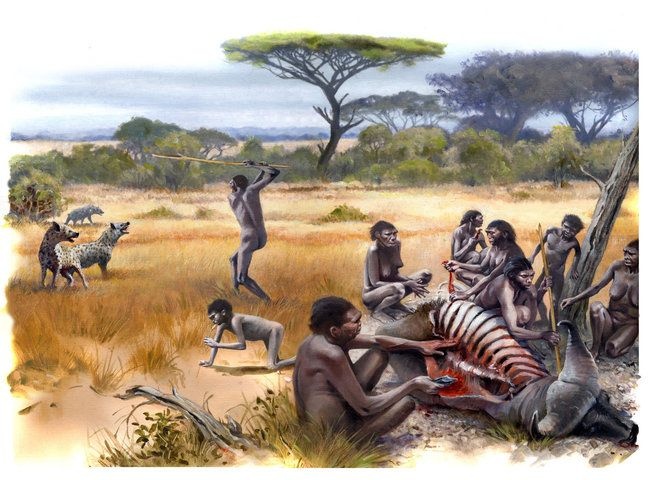
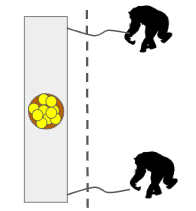
A cooperation game that simulates the challenge of our stone age ancestors to acquire food in the African savanna
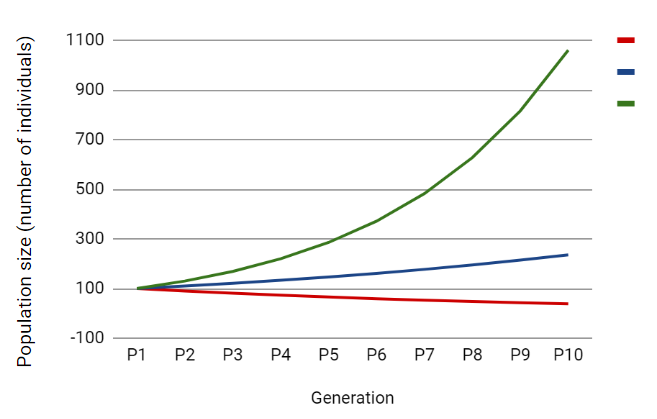
A worksheet in which students calculate and graph the changes in the frequencies of traits related to cooperative foraging in a population over several
A fill in the blanks activity on the natural selection of traits that enabled cooperative foraging in our ancestors
A reading text about cooperative foraging in the animal kingdom and in our early ancestors
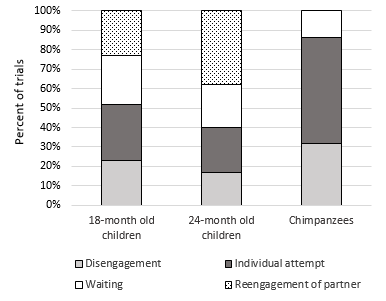
A series of experiments with small children and chimpanzees to investigate their ability and motivation to engage in collaborative activities
In this short video, we observe how chimpanzees seem to be unable to spontaneously coordinate their activities to get food – something that humans
In a series of experiments, anthropologists wanted to find out whether chimpanzees and bonobos work together and share a common source of food. Results
All causal maps on human evolution in one Google slide file
Materials for constructing causal maps about the evolution of human traits on the blackboard
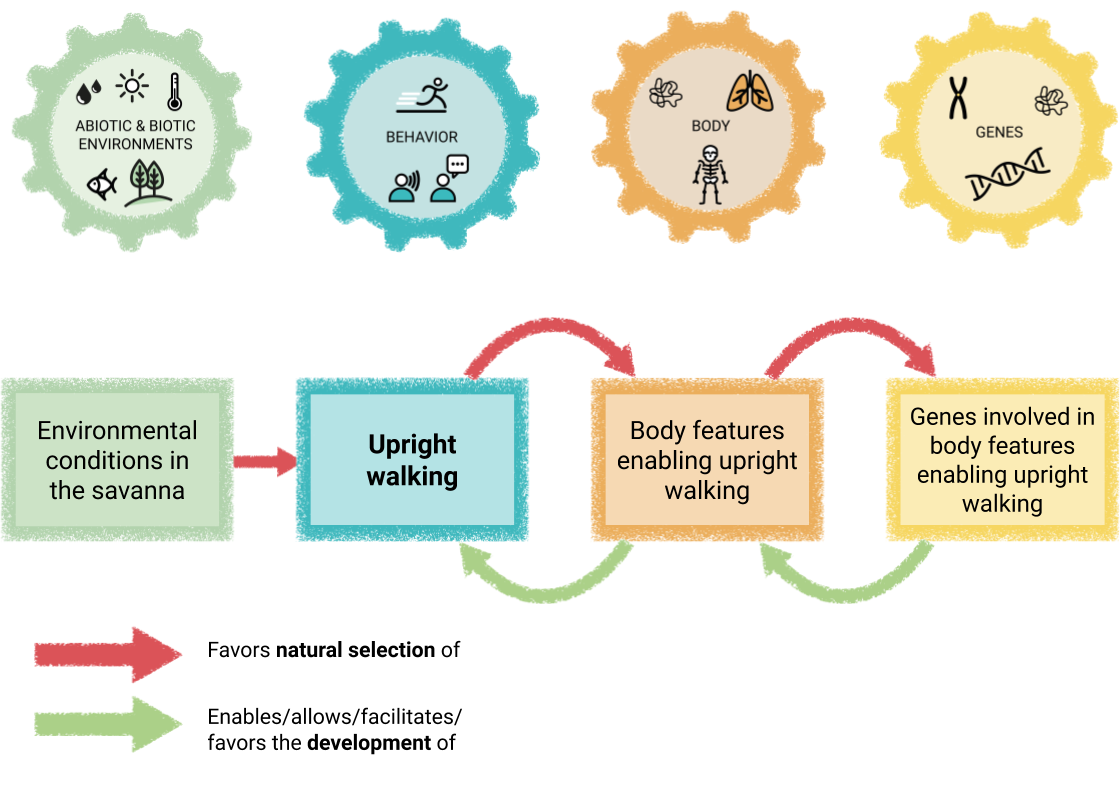
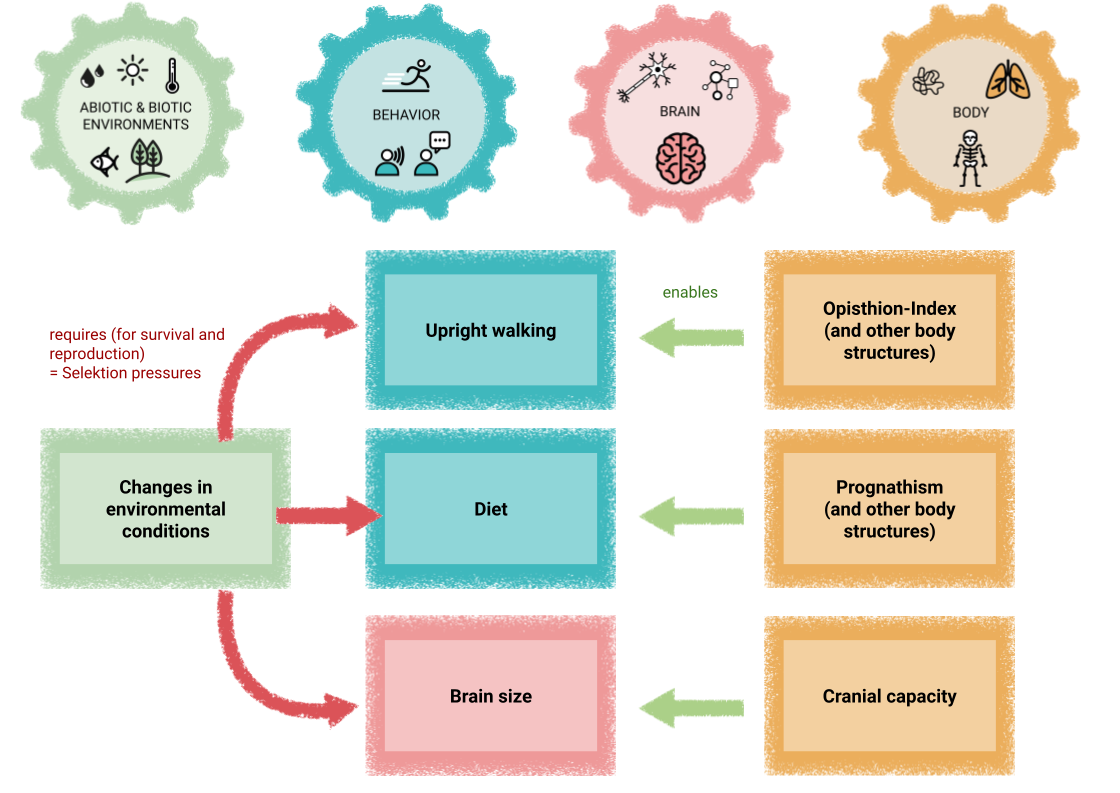
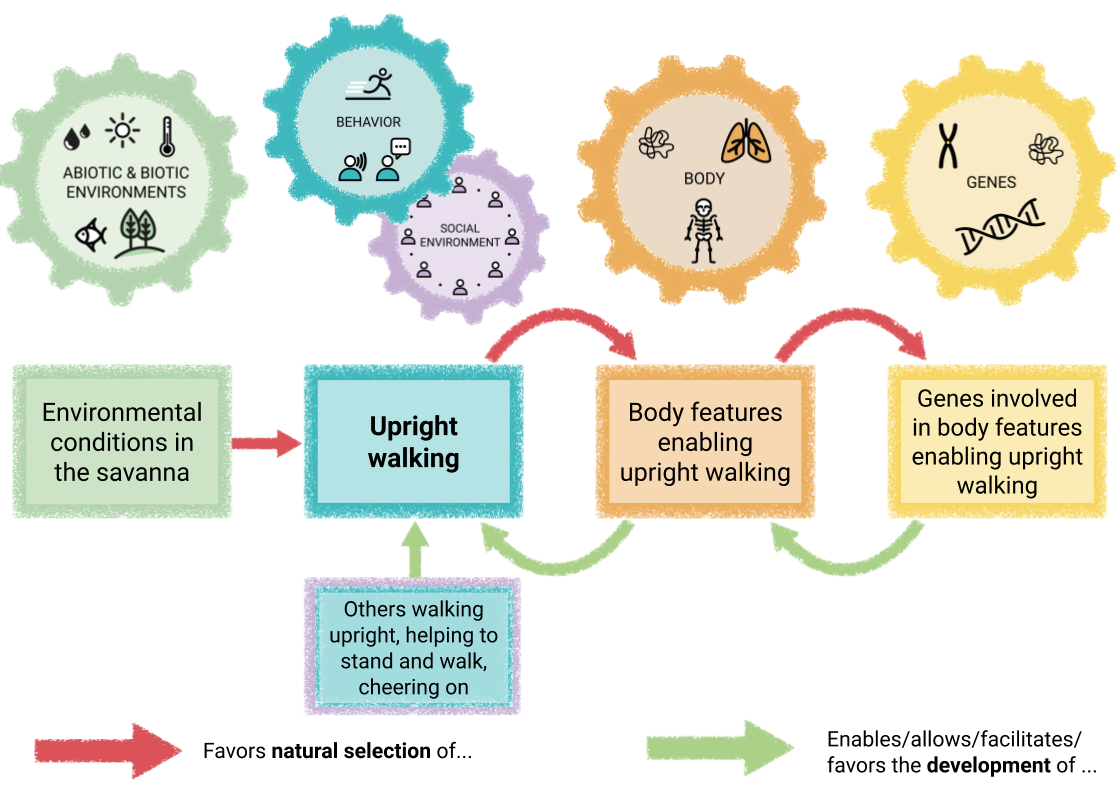
Chalkboard materials for constructing a causal map for the evolution of upright walking
A handout that introduces students to the causal map to map the evolution and development of traits, with the example of upright walking
A worksheet in which students calculate and graph the changes in the frequencies of traits related to upright walking in a population over several
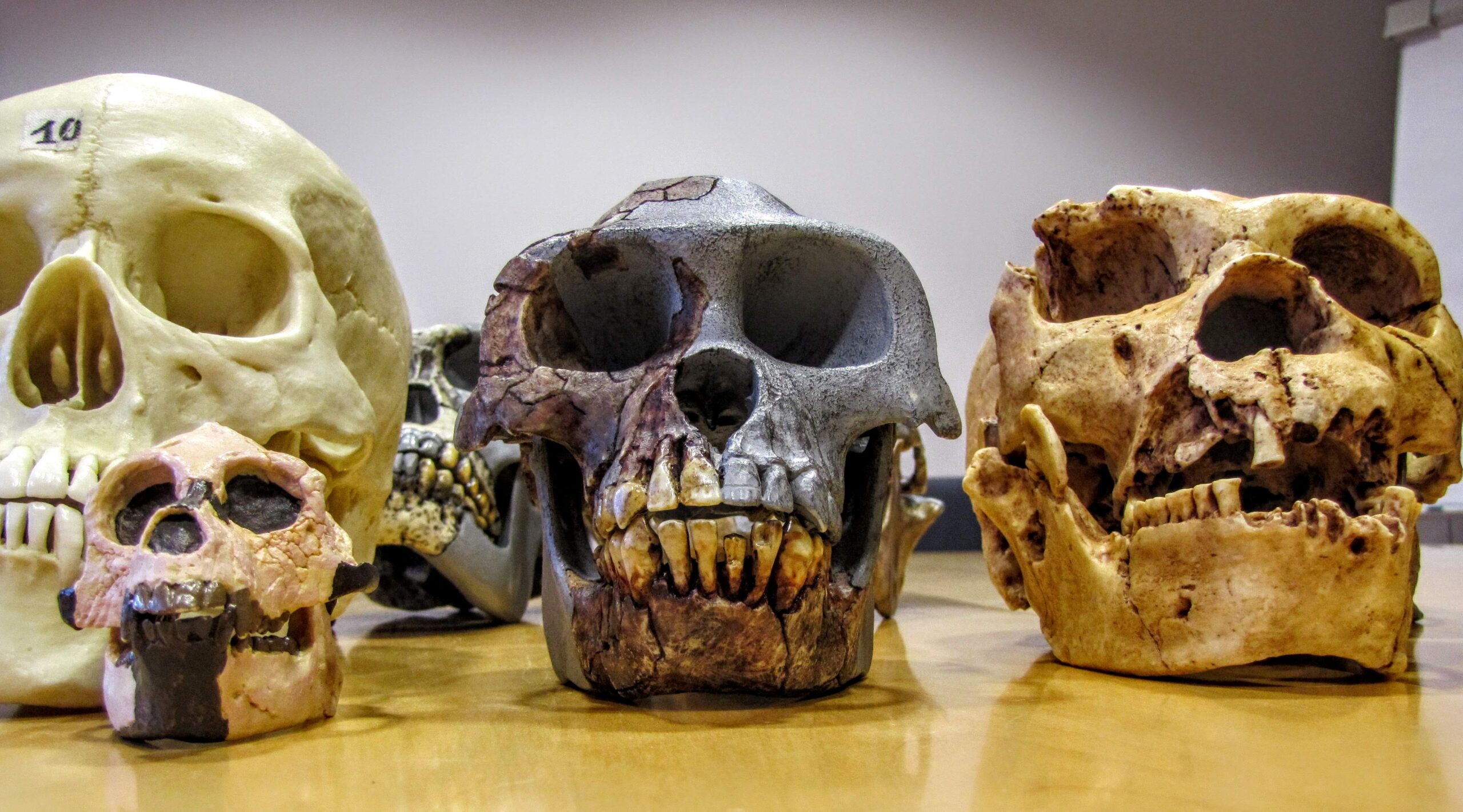
Google sheet template for entering and plotting the measurements of hominin fossil skulls
Instruction sheet for measuring cranial capacity, opisthion index and prognathism on fossil hominin skulls
Materials for constructing an initial causal map relating observable features of fossil hominin skulls, behaviors, and environmental conditions
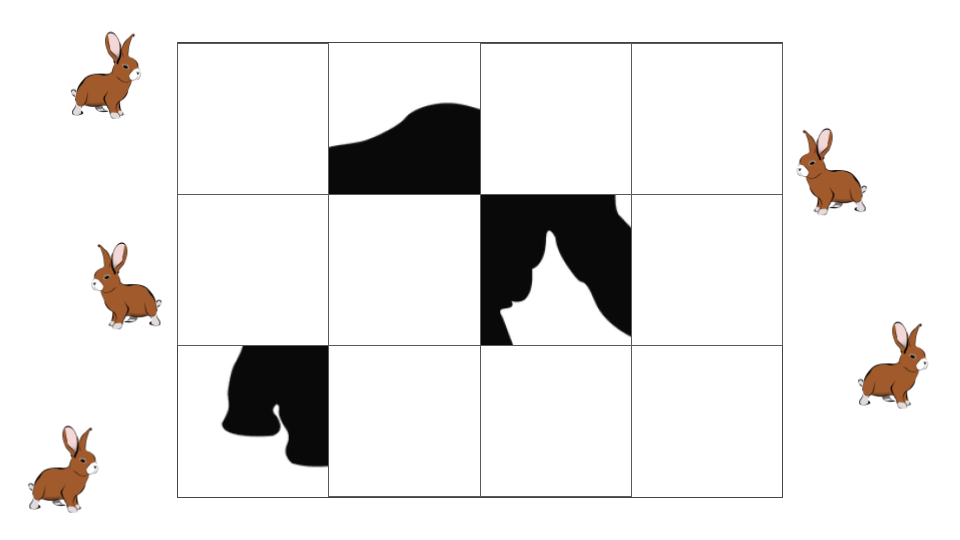
An activity for students to explore and notice traits on fossil hominin skulls
Human intelligence seems to be a social, more than merely an individual phenomenon. What can we learn from comparing human societies to human brains?
The human brain is the seat of human agency, and yet this agency is caused by cellular agents unaware of our larger human goals.
A collection of lesson materials to explore the nature of human morality in the light of evolution and sustainability
Thinking tools are used across diverse lessons to develop the skills of evolutionary anthropologists, behavioral scientists, and sustainability scientists
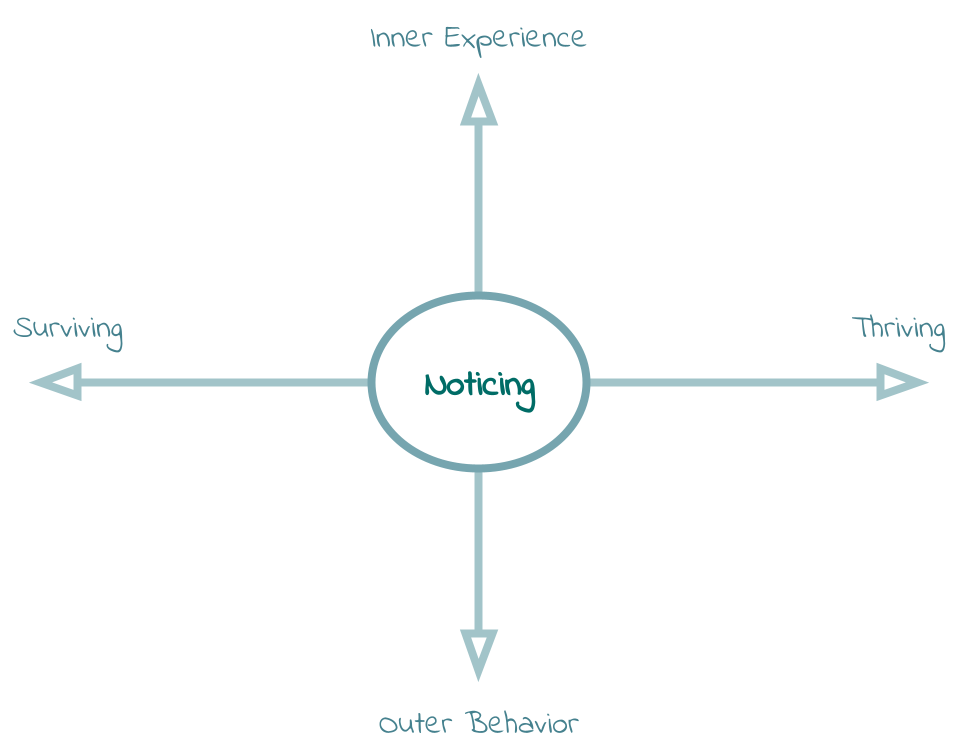
The Noticing Tool helps us be aware of and interpret our experiences and behaviors in the present and to orient our behaviors towards valued
How should we think about the actions and functions of machines in society? How can a science of machine behavior help us understand and
Classroom resources for exploring (the evolution of) human needs, values, and well-being
Human Evolution Resources Cumulative Culture Physicist Isaac Newton once said of the importance of his scientific accomplishments: “I could only look so far because
What can we learn from cooperation games about human evolution, behavior, and sustainability? Cooperation games help us to investigate the causes, variations, and consequences
A page for researchers interested in the concept of agency as it relates to learning theories of evolution, including natural selection in biological systems.
Learning and Evolution are processes that are both similar and different, in important respects. What can humans learn by comparing these processes?
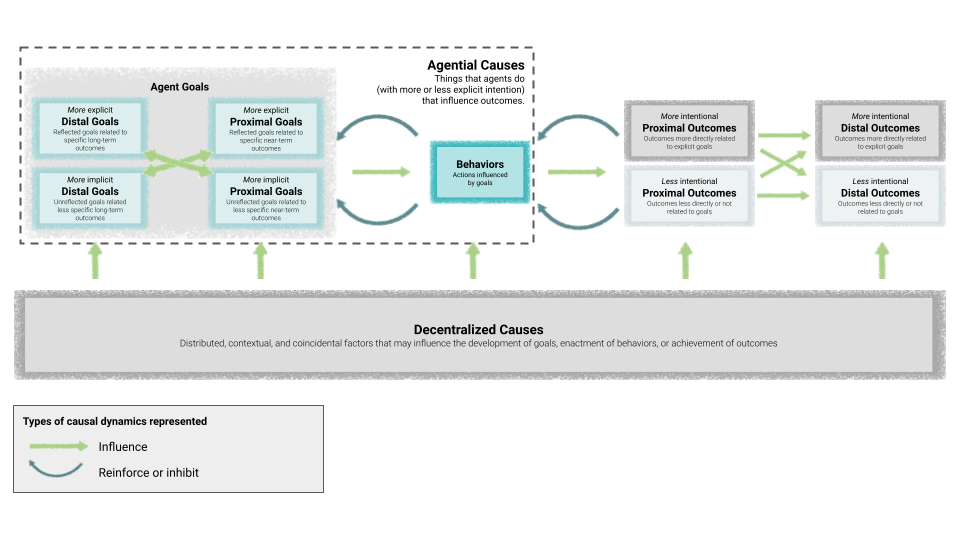
How can we understand the causal relationships between goals, behaviors, and outcomes?
An introductory h5p interactive sorting task for starting a conversation on the diversity and complexity of understanding agency.
An introduction to Michael Levin’s framework for understanding agency across biological and computational contexts.
‘What Kind of Mind?’ provides teaching resources to introduce pupils to research ideas about animal minds.
A collection of interactive H5P activities around the themes of evolution, behavior, sustainability
An Evolving Schools Regional Workshop Model on the participatory development of school profiles that can inform school improvement and global innovation research collaborations.
In this lesson students explore the concept of (human) behavior, its causes, and its relation to well-being and sustainable development.
Resources for advancing a regional workshop on the topic of curriculum overload.
Regional Workshop Models are collections of resources and ideas for teacher education and school innovation research groups to organize around as part of local
A collection of resources for understanding the evolutionary origins and cultural diversity of number systems and ways of quantifying the world around us.
The OpenEvo TeachingBase provides a roadmap to our interdisciplinary collection of teaching resources.
This model simulates the evolution of populations in an environment that is spatially structured. In such a situation, several evolutionary mechanisms operate, including migration,
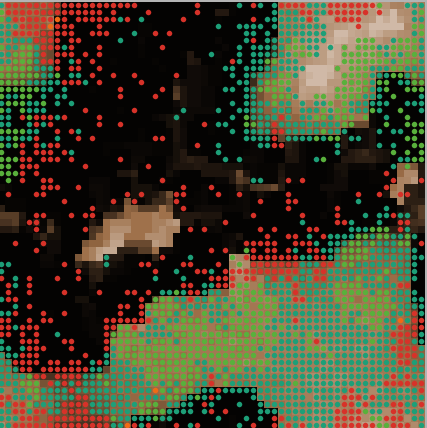
This model adds cultural evolutionary dynamics through behavior imitation to the evolution of resource use behavior.
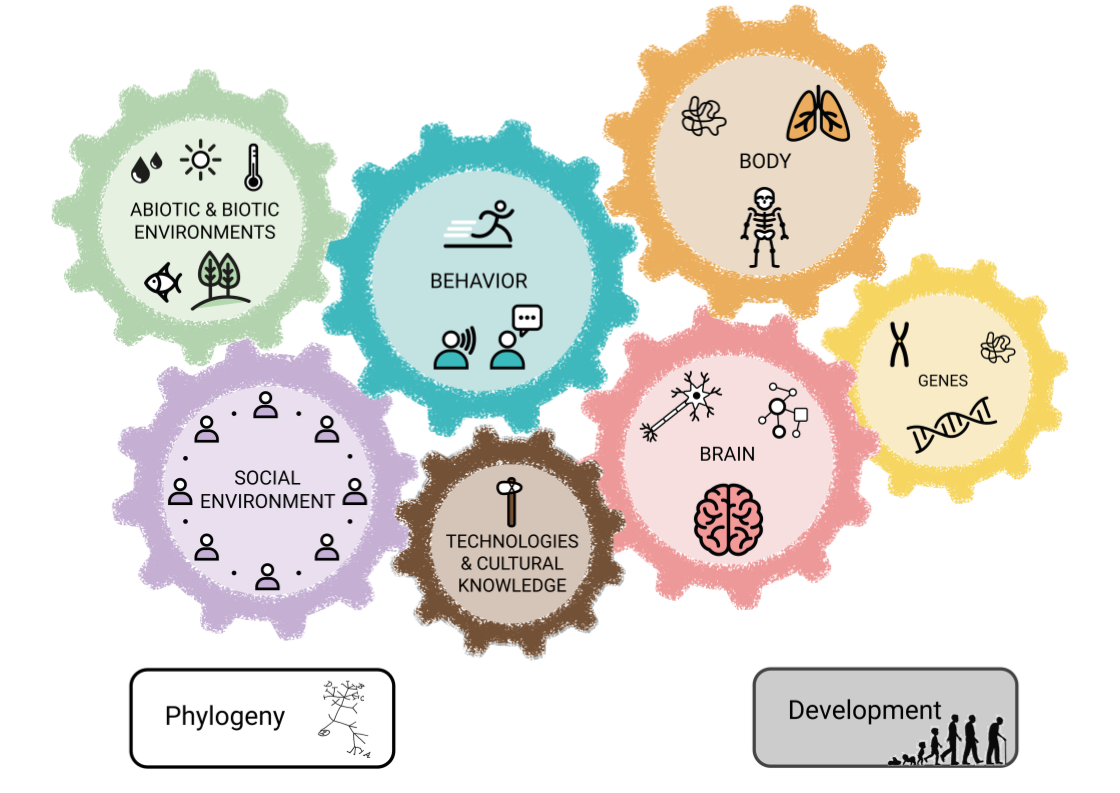
Simple diagrams can help us map and understand the structures of knowledge in our world.
Learning about Structures of Knowledge (SoK) is a foundation for interdisciplinary learning. SoK can be represented graphically in diagrams that help us understand and
The scientific fields of evolutionary anthropology and behavioral sciences have produced a wealth of new insights into the nature of human behavior, cognition and
This model lets us explore how the appearance of certain social behaviors can affect evolutionary population dynamics.
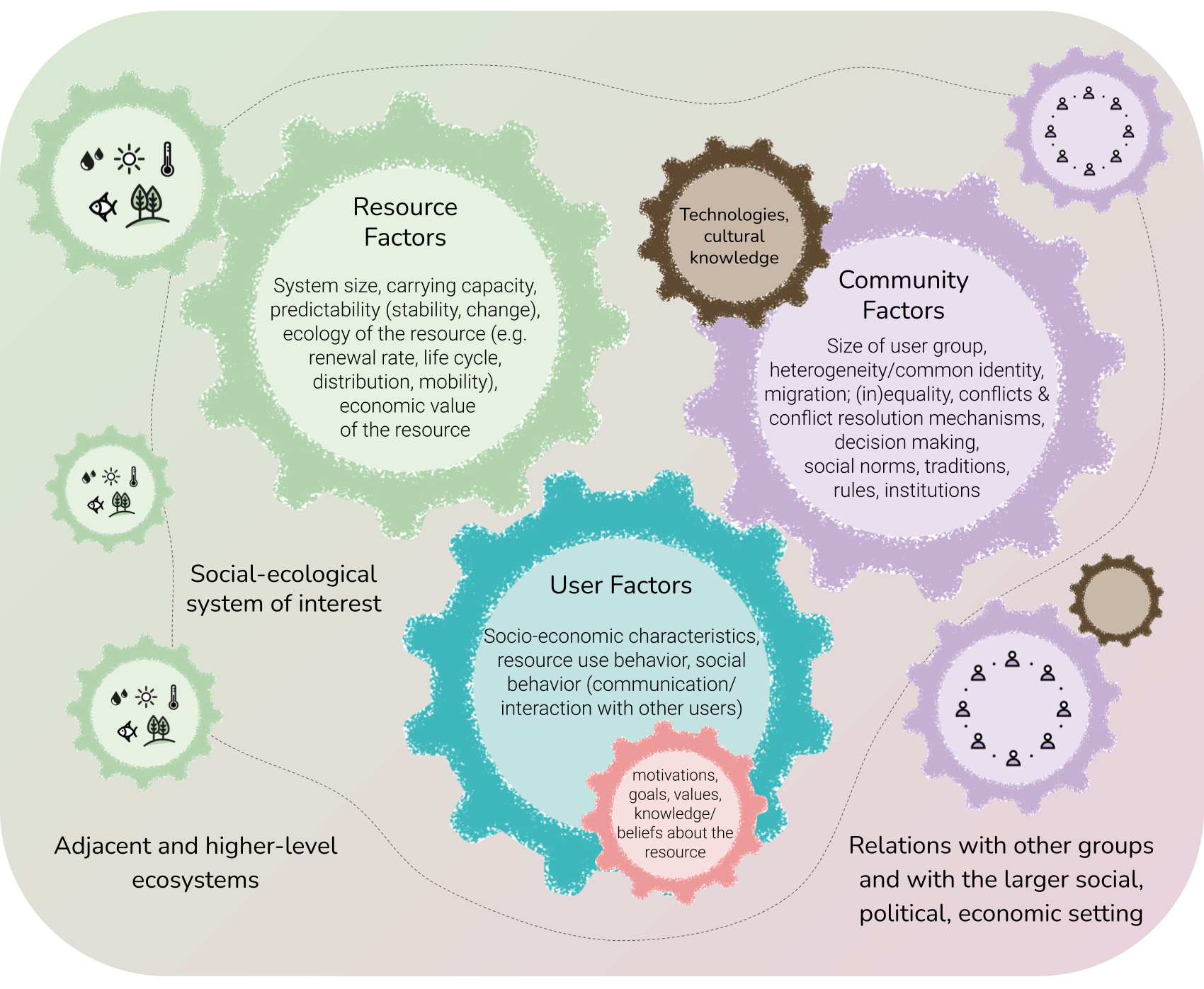
In this lesson, students analyze a select real-world social-ecological system by looking at factors of the resource(s) and ecosystem, resource user behaviors, and governance,
A lesson collection on evolution, cooperation, and sustainability
Evolutionary Anthropology in the Primary School – a pre-service primary teacher module
The core self-study module for entering the Prosocial Youth ecosystem of ideas and resources.
Our interdisciplinary teacher’s guide outlines our educational design concept. It provides introductory readings around core concepts of human sciences and ideas for exploring them
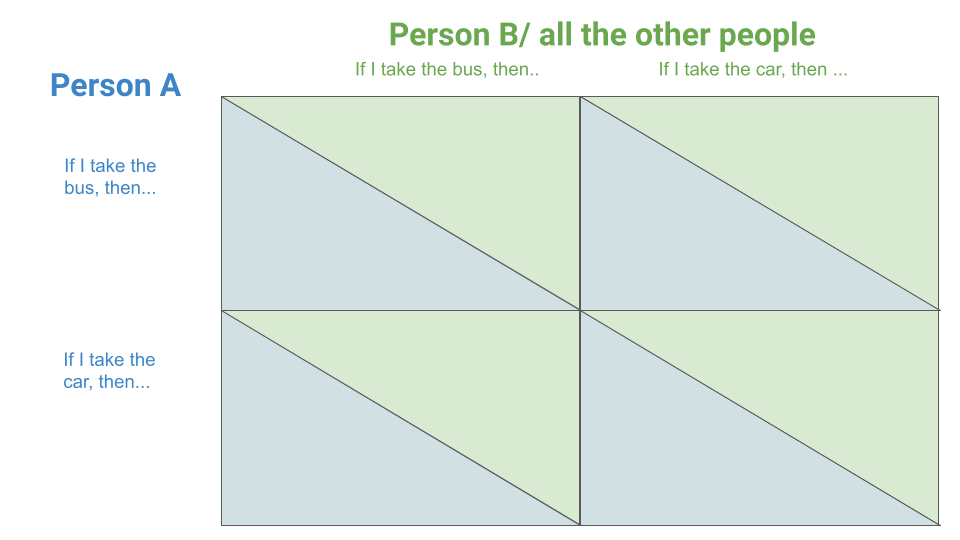
Payoff matrices can help us analyze the behavioral strategies and possible outcomes in diverse situations across biology and society.
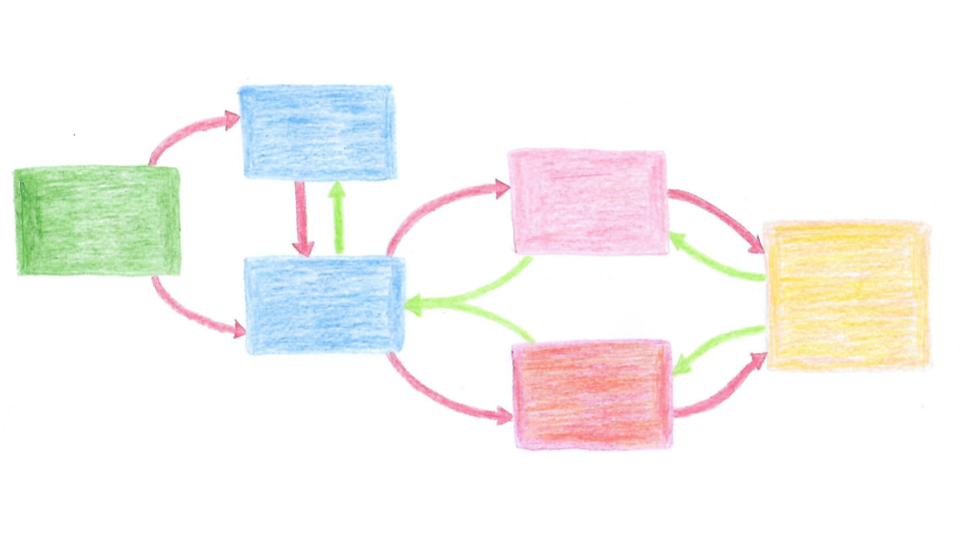
Causal mapping helps us reflect on the interdependent relationships within complex systems
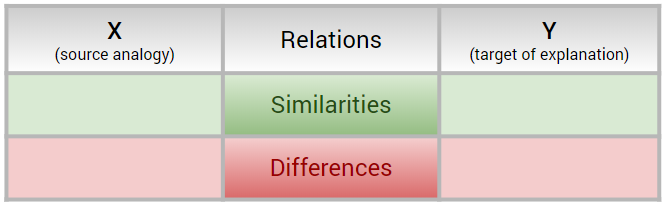
Analogy mapping is a tool for thinking about similarities and differences between different concepts or phenomena.
Dustin Eirdosh is a researcher in the Department of Comparative Cultural Psychology at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Psychology, in Leipzig, Germany and
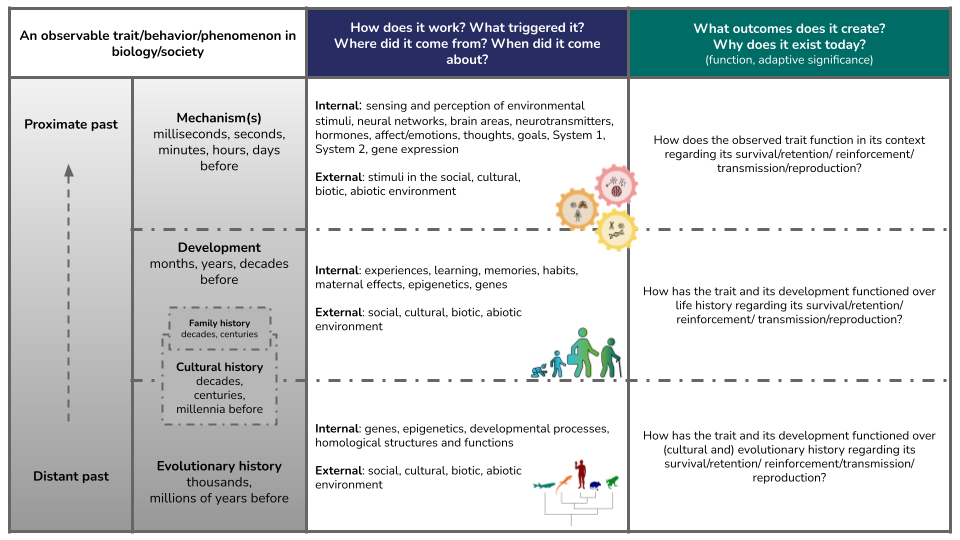
Tinbergen’s Questions can help organize complex causality of behaviors and other phenomena across time.
How can we use insights about human evolution, human behavior, and the causal interactions in social-ecological systems to address local, regional and global sustainability
What can we learn from our own thoughts and intuitions about human evolution, behavior, and sustainability? Understanding the causes of our perceptions, intuitions, and
What can we learn from computer models about human evolution, behavior, and sustainability? Computer models allow us to observe and investigate the influence of
What can we learn from communities around the world managing shared resources about human evolution, behavior, and sustainability? Exploring diverse sustainability dilemmas in the
What can we learn from the diversity of human cultures about human evolution, behavior and sustainability? Studying the behaviors of humans around the world
What can we learn from children about human evolution, behavior, and sustainability? The development of social and cognitive abilities in the course of a
What can we learn from our biologically close and distant relatives about human evolution, behavior, and sustainability? Comparing traits of humans and other species
What can we learn from our ancestors about human evolution, behavior and sustainability? Exploring the characteristics of our ancestors, their living conditions, and the
Schools are central social environments for young people to grow and develop themselves. How schools are governed, and which norms, values, and institutions get
Human Evolution Resources Life with other groups The evolution and history of our species is not only characterized by living in isolated and small