TeachingBase
Human Behavior & Sustainable Development
The theme of human behavior holds many possibilities for teachers to develop interdisciplinary learning opportunities. Many themes in the curricula of subject areas deal with human behavior explicitly or implicitly. Many objectives of education in general, and of education for sustainable development in particular, aim to promote in students the ability to act responsibly, to take the perspectives of others, and to develop social-emotional competencies. At the same time, many social problems, from xenophobia to mental health, to problems of sustainable resource use, have in common that they are causes and consequences of human behavior. Furthermore, we humans, across cultures, generally have a great interest in human behavior – intuitively and almost every second we perceive human behavior in everyday life.
In this module, we therefore explore how we can convey the diverse concepts, research methods, and insights of the interdisciplinary behavioral sciences (including behavioral ecology and biology, behavioral economics, evolutionary anthropology, psychology, sociology) within individual subject areas, as well as for interdisciplinary teaching.

- Grade or expertise levels Teacher education, Undergraduate
- Language(s) English, German
- Learning Goals Conceptual Thinking, Cooperation Competency, Critical Thinking, Design Thinking, Evaluation Competency, Evolutionary Thinking, Future Thinking, Growth Mindset, Intellectual Humility, Intercultural Competence, Interdisciplinary Thinking, Metacognitive Competency, Self-Regulation Competency, Systems Thinking
Teaching Materials
“Fair” does not always mean the same thing
These lesson materials introduce students to issues of fairness and various interpretations of it. Reflecting on results of a cross-cultural experiment with children, students discuss how we can use our understandings to create a more fair world.

A Teacher’s Guide to Evolution, Behavior, and Sustainability Science
Our interdisciplinary teacher’s guide outlines our educational design concept. It provides introductory readings around core concepts of human sciences and ideas for exploring them in the classroom.
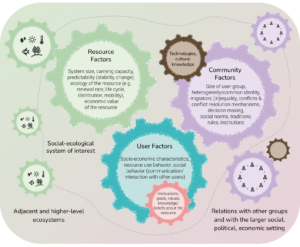
Analyzing social-ecological systems
In this lesson, students analyze a select real-world social-ecological system by looking at factors of the resource(s) and ecosystem, resource user behaviors, and governance, to develop recommendations for improving the sustainable management of the resource.

Backwards Brain Bicycle
This video is about a bicycle that works differently than normal bicycles, and how challenging it is for our minds to learn how to ride this new bicycle.
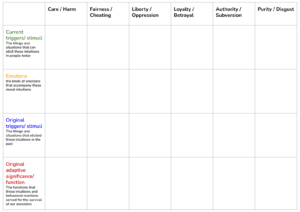
Causes of our moral intuitions
In this lesson students explore the causes of our moral intuitions with the help of a sorting activity and reflection questions.
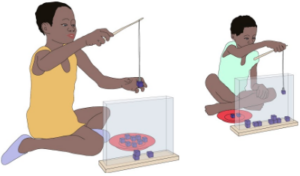
Chimps or children – who is better at sharing resources?
A comparative behavioral research experiment exploring the abilities of chimpanzees and of children to cooperate around a shared resource.
Climate Change Game
A cooperation game that lets students experience some of the challenges of cooperation in addressing global climate change
Collective Action Puzzle Game
A group game that lets students experience the dilemma between self-interest and collective interest when groups have to work together to achieve shared goals.

Commons game
In a classroom simulation game with changing conditions students develop strategies for the use of a common resource so that the profit for the entire group is maximized.

Cultural evolution (lesson plan)
Students explore the concept of cultural evolution by comparing it to genetic evolution based on a number of concepts, and explore why cultural evolution is so important in our species.
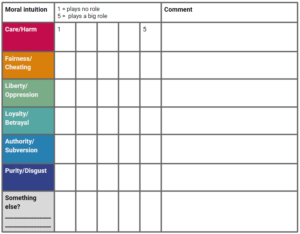
Discussion guide about moral issues
Lesson plan and worksheets to apply understandings of moral psychology in classroom discussions about ethical issues
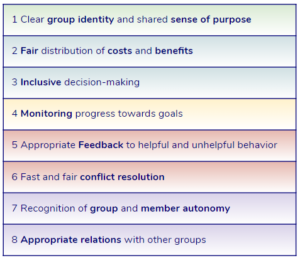
Exploring the Design Principles for Cooperation
Students explore the principles that allow groups to work together and achieve common goals, applying them to the groups that they are a part of or care about.

Exploring values
This lesson is about exploring the concept of values with students and having them identify and reflect on what they personally value, or what makes their life meaningful.

Fast thinking or slow thinking
In this lesson students sort their own experience of thinking into fast and slow processes. Based on this, they come to understand that our thinking is shaped through experience such that things we do often and regularly become easier over time.
Function of cognitive biases
In this lesson students learn about the concept of cognitive biases as well as a number of important cognitive biases that may affect our well-being and social interactions, identify their causes in evolutionary history, their functions, and reflect on how to cope with cognitive biases.

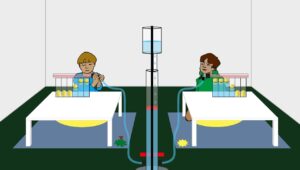
Game theory: Ultimatum and Dictator game
A set of behavioral experiments across cultures that explore the human sense of fairness.

Honeybee Democracy
Students explore how a honeybee swarm makes a decision about their future nesting site, and explore the similarities and differences to how human groups make decisions.

Introduction to social dilemmas and the payoff matrix
Students reflect on the causes and consequences of human behaviors in situations of social interactions, and are introduced to the payoff matrix as a helpful tool to represent motivations and outcomes of behaviors.
Life in groups and conflict resolution
A reading text about the challenges of life in groups and how groups across biology have found ways to solve these challenges.

Lost wallet study
A behavioral experiment across 40 countries that explored human motivations to return lost wallets to their owner

Mismatch? (lesson plan)
Students learn about the concept of evolutionary mismatch and apply it to various problems of sustainable development.
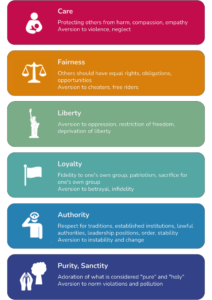
Moral intuitions handout
An overview of six important human moral intuitions

Moral taste buds
In this lesson students explore the causes and functions of, as well as ways to flexibly relate to our moral intuitions by engaging the analogy to our taste buds.
NetLogo Model: Evolution and competition for resources (abstract)
This NetLogo model lets students explore how competition for resources can affect the evolution of a population and can result in resource overuse. This model is similar to the Evolution and competition for forest resources model, but more abstract.

NetLogo: Evolution and competition for forest resources
This NetLogo model builds on the model of Two Foresters. In this model, agents reproduce based on the amount of resources that they harvest.

NetLogo: Evolution of ethnocentrism
This model simulates the biological evolution of ethnocentrism in a population made up of multiple ethnicities.

NetLogo: Evolution of resource use and social behavior (monitoring and punishment)
This model lets us explore how the appearance of certain social behaviors can affect evolutionary population dynamics.

NetLogo: Evolution of resource use through behavior imitation
This model adds cultural evolutionary dynamics through behavior imitation to the evolution of resource use behavior.

NetLogo: Evolution of resource use with harvest efficiency
This model introduces the concept of resource use efficiency into the evolution of resource use behavior.

NetLogo: Two communities
This NetLogo computer model extends the model Two Foresters and introduces a bigger and more complex population structure

NetLogo: Two Foresters
An interactive introduction into concepts of ecology, behavioral ecology, and sustainability with a computer simulation of a simple social-ecological system.

Noticing moral intuitions
Students identify the moral intuitions underlying people’s opinions in quoted texts and images.

OpenEvo Guide to Using AI Tools for Lesson Development
This document is intended to give you some ideas on how you can use Artificial Intelligence (AI) to design a lesson or unit that integrates competencies in Education for Sustainable Development, concepts of human behavior and behavioral science, and topics of sustainable development.
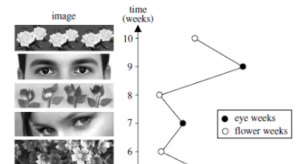
Perception of eyes and prosocial behavior
A behavioral experiment that tells us about the role of unconscious perception, particularly the perception of human eyes, on human social behavior.
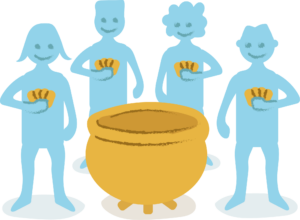
Public Goods Game
With these teaching materials, students can be introduced to game theory in general, as well as a concrete method, the public goods game. The conditions and rules of the public goods game reflect the challenge of a group to maintain common resources.
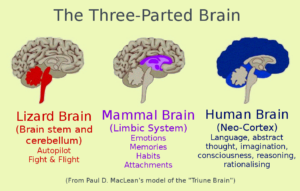
Reading text – brain areas and their functions
A handout about the “Triune Brain” model highlighting different functions of different brain regions
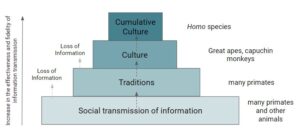
Reading text: Cumulative culture
A reading text about the importance of cumulative culture in our everyday experience and in the evolution of our species
Stone Age Hunting Game
A cooperation game that simulates the challenge of our stone age ancestors to acquire food in the African savanna
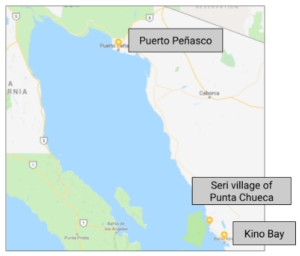
Three Mexican fisheries
Students compare the stories of three Mexican fishing villages to understand the factors that enabled some villages to sustainably manage their fishing resources, while others failed.

True stories of people who left radical movements
In this unit students explore stories of people who have left a radical movement, or deliberately discuss with representatives of the “other side” and build respectful relationships. These let us explore the circumstances, experiences and insights about why prejudice, hatred and violence against other people or a group can arise and how they can dissolve again.

Two stories of capitalism
Students explore two contrasting stories about the benefits and failures of capitalism, identify the moral intuitions behind each story, and write a third story about capitalism that integrates aspects of both stories.

What is behavior?
In this lesson students explore the concept of (human) behavior, its causes, and its relation to well-being and sustainable development.
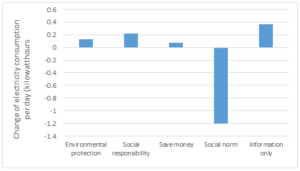
What motivates people to save energy
A set of behavioral experiments to find out what motivates people to save electricity, exploring the roles of monetary incentives, social norms, appeals to the environment or to citizenship.

