Human Evolution Resources
What does it mean to be human?
Our collection of resources for learning about human origins provides a foundation for exploring the big questions about our species
Our human characteristics are the result of evolutionary history, culture, individual development
Evolution is the change of trait frequencies in a population. This change is the result of interactions between the abiotic, biotic and social environments, behaviors, bodies, brains, technologies, cultures, and genes of organisms. These interactions cause populations to change over time, as new features arise, some features become more common and others become more rare. These interactions therefore shape the evolution and development of our traits and our world.
Different scientists define and study evolution in different ways. Some are primarily interested in the change of genotypes and gene frequencies in a population. Others also look at change in many other things (phenotypes, e.g. behaviors, brains, bodies, social organisation, technologies, culture, and environmental features) in a population (see comparison table in Cultural Evolution). Depending on what we look at, there can be different ways that traits get inherited, transmitted or retained in a population – for example, through the inheritance of genes to offspring, or through imitation of behaviors. There can also be different ways how new variations of traits appear in the population, and different ways through which some traits become more common and others less common in a population.
If we want to understand the evolution of human behaviors and cultures, it makes sense to look at many different phenotypes and their interactions, and consider all of the possible mechanisms of their variation, selection, and inheritance.
Themes in the evolution of human behavior, cognition, and culture
Below you will find links to thematic content pages, each page provides a range of online resources and ideas for teaching activities. We continue to collaborate with students, teachers, and classrooms around the world to curate and develop new ideas for understanding human evolution! Explore the pages below and contact us with questions or ideas for further resource development.
Humans are living beings, mammals, primates
- Gene-Culture Co-Evolution
Here you find a collection of various teaching materials (worksheets, handouts, lesson plans etc.) for exploring the evolution of human traits.
Born good? Babies help unlock the origins of morality
Can infants already distinguish between what is morally right and wrong? This video explores experiments with babies to answer these questions.

Human Origins Lab
The Human Origins Lab from Ancient Ancestors.

Observing differences in hominin skulls
An activity for students to explore and notice traits on fossil hominin skulls
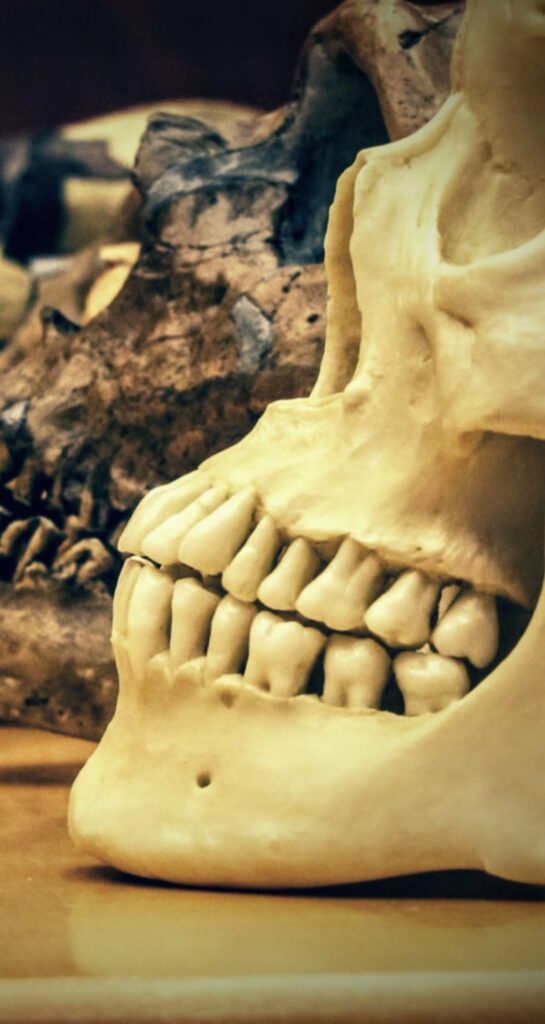
Causal map materials for skull morphology and related traits
Materials for constructing an initial causal map relating observable features of fossil hominin skulls, behaviors, and environmental conditions

Hominin skull measurement instructions
Instruction sheet for measuring cranial capacity, opisthion index and prognathism on fossil hominin skulls

Hominin skull measurement Google sheet for data entry and analysis
Google sheet template for entering and plotting the measurements of hominin fossil skulls

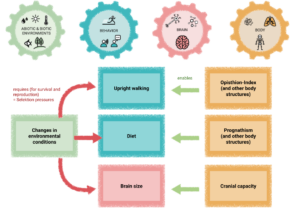
Worksheet: Natural selection of upright walking
A worksheet in which students calculate and graph the changes in the frequencies of traits related to upright walking in a population over several generations, exploring the role of variation, fitness consequences and trait inheritance in evolutionary change.
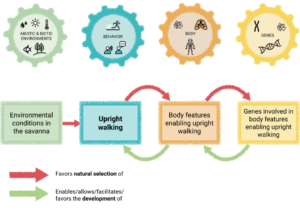
Handout: Introduction to causal maps with the example of upright walking
A handout that introduces students to the causal map to map the evolution and development of traits, with the example of upright walking

Chalkboard materials: Causal map on upright walking
Chalkboard materials for constructing a causal map for the evolution of upright walking
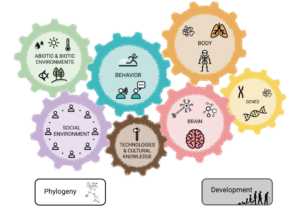
Blackboard materials: Causal maps on human evolution
Materials for constructing causal maps about the evolution of human traits on the blackboard

Causal maps on the evolution of human traits
All causal maps on human evolution in one Google slide file
Worksheets: Cooperation experiments with chimps and bonobos
In a series of experiments, anthropologists wanted to find out whether chimpanzees and bonobos work together and share a common source of food. Results tell us something about the role of social tolerance in cooperative foraging.

Video – Can chimpanzees coordinate their activities
In this short video, we observe how chimpanzees seem to be unable to spontaneously coordinate their activities to get food – something that humans find very easy.
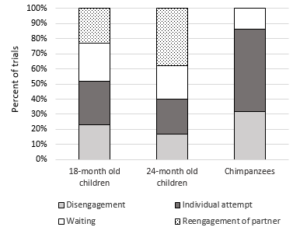
Cooperative activities with children and chimpanzees
A series of experiments with small children and chimpanzees to investigate their ability and motivation to engage in collaborative activities

Reading text: Cooperative foraging
A reading text about cooperative foraging in the animal kingdom and in our early ancestors

Fill in the blanks: adaptations to cooperative foraging
A fill in the blanks activity on the natural selection of traits that enabled cooperative foraging in our ancestors

Worksheet: Natural selection of traits for cooperative foraging
A worksheet in which students calculate and graph the changes in the frequencies of traits related to cooperative foraging in a population over several generations, exploring the role of variation, fitness consequences and trait inheritance in evolutionary change.
Stone Age Hunting Game
A cooperation game that simulates the challenge of our stone age ancestors to acquire food in the African savanna

Reading text: Tool making and human evolution
A reading text about tool use and tool making in the animal kingdom and in our early ancestors

Video questions – Kanzi making and using stone tools
The bonobo Kanzi was taught to make and use simple stone tools of the Oldowan culture. What can we conclude about the mental abilities of Homo habilis from Kanzi’s performance?
Video questions: Breeding foxes and social temperament
This video is about domestication – or “taming by breeding” – of foxes, a Russian research project that has been conducted since the 1950s. It shows which behavioral patterns of foxes were selected during breeding, what was found out about the genetic makeup underlying these patterns of behavior and to what extent fox breeding is comparable to the breeding of dogs.
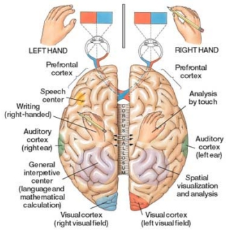
Reading text – Brain and coordination of body movements
A reading text on the evolution of left-right handedness and the role of the brain

Imitation in chimps and children (Video, Experiment)
A series of experiments to explore the tendency to imitate in children and chimpanzees
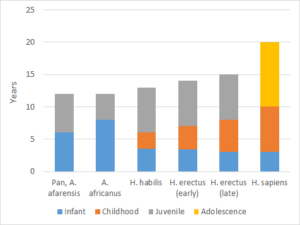
Reading text – Evolution of childhood
A reading text and causal mapping tasks on the (co)evolution of brain size, childhood, premature birth, cooperative childcare and social learning and teaching
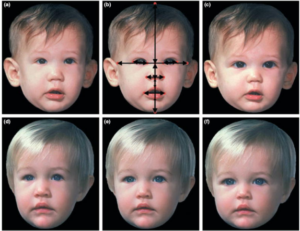
Reading text – Baby schema
A reading text on the evolution of the baby schema together with cooperative child care

Video: the pointing gesture
A video excerpt and worksheet on the importance of pointing gestures in human communication

Video, Worksheets: Experiments on the social behavior of babies
Using puppets psychologists explore what small children as young as a few months old think about their social environment and whether they can distinguish between “good” and “bad”.
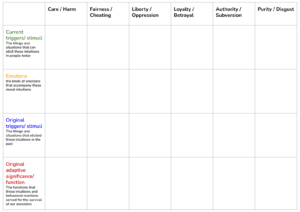
Causes of our moral intuitions
In this lesson students explore the causes of our moral intuitions with the help of a sorting activity and reflection questions.
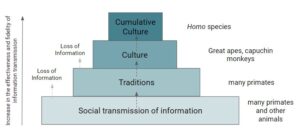
Reading text: Cumulative culture
A reading text about the importance of cumulative culture in our everyday experience and in the evolution of our species
Lost explorers
Stories of lost explorers that tell us about the importance of cultural knowledge to our survival.

Cultural evolution (lesson plan)
Students explore the concept of cultural evolution by comparing it to genetic evolution based on a number of concepts, and explore why cultural evolution is so important in our species.
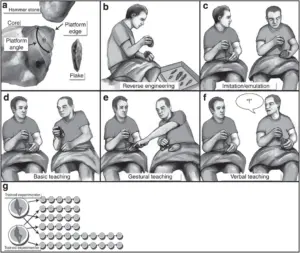
Experiment on the the co-evolution of tool making, teaching, and language
An experiment in which researchers wanted to examine the role of teaching and communication in the transmission of toolmaking.

Mismatch? (lesson plan)
Students learn about the concept of evolutionary mismatch and apply it to various problems of sustainable development.
Values domains sorting activity
This activity lets students explore the six different values domains by considering why we humans might have evolved to find these areas of life meaningful and important, and what kinds of different things we can do to live towards these valued domains.
Worksheet: Fossil hominin fact sheet
A worksheet on which students collect information on a specific fossil hominin
Lesson plan: Evolution and development of upright walking
This document contains a collection of activities and resources related to the evolution and development of upright walking in our species
Partner projects with relevant resources

Ancient Ancestors
AncientAncestors develops inquiry-based educational labs on human evolution and studies their impact on students’ knowledge acquisition.

EvoKids.de
The original German EvoKids project. Knowledge of evolution is of central importance for the modern worldview. Therefore, children should learn as early as possible how the different forms of life on earth have developed. For this reason, the “Evokids” project is committed to ensuring that the important topic of “evolution” is not only taught in the 10th grade – as has been the case up to now – but already in elementary school.

Human Evolution Teaching Materials Project
The Human Evolution Teaching Materials Project (HETMP) provides resources for middle and high school educators to facilitate the inclusion of human evolution into existing science curricula. HETMP was designed to help teachers generate 3D models of hominin fossil crania and provide accompanying lesson plans, increasing access to
‘hands-on’ learning materials.

What Kind of Mind?
‘What Kind of Mind?’ provides teaching resources to introduce pupils to research ideas about animal minds.

