Life with other groups
The evolution and history of our species is not only characterized by living in isolated and small hunter-gatherer groups, in which everyone knows each other and has personal contact. Our human traits have also been shaped by competition and cooperation between groups, and finally by the fusion into ever larger groups.
Cooperative exchange between groups
Competition and Cooperation between groups: from sociality to ultrasociality
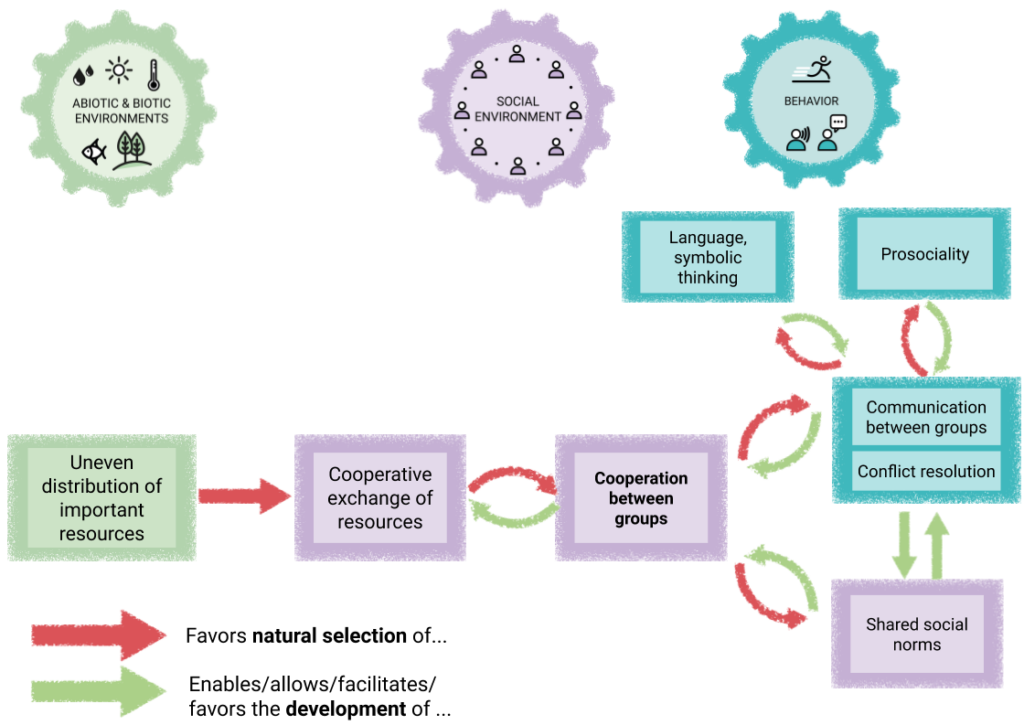
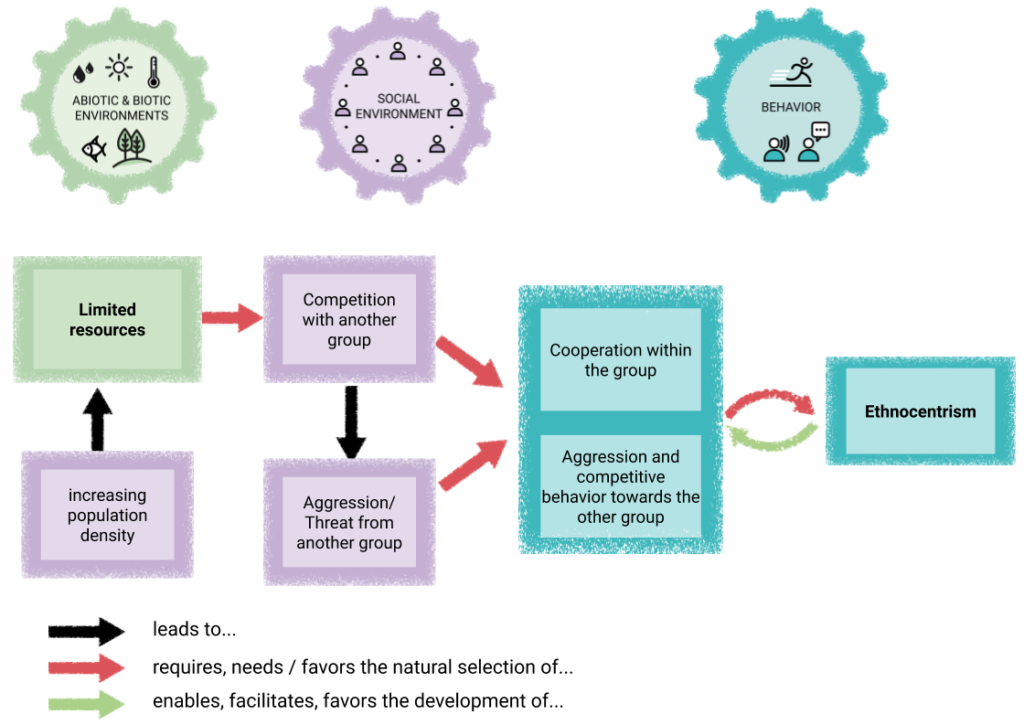
When groups meet and compete with each other, e.g. because certain resources are limited, those who can unite into one entity and cooperate within the group will be at an advantage.
Competition between groups exists in many species. However, in our species this competition apparently lead to the fact that, within a relatively short time in evolutionary terms, we were able to “merge our boats” with those of other groups, into ever larger groups that “steered a boat together”.
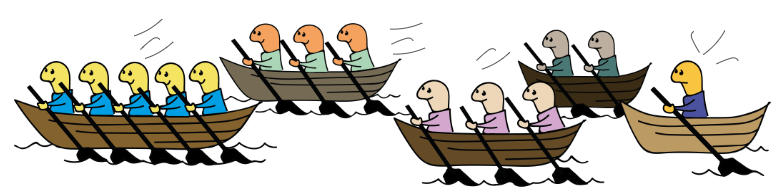
“Sticks in a bundle are unbreakable.”
Kenyan proverb
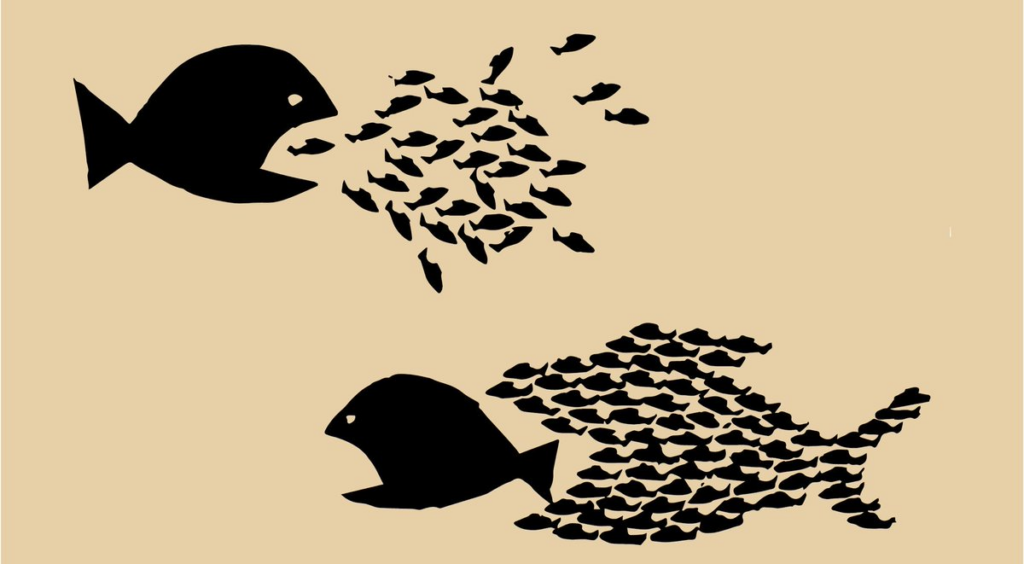

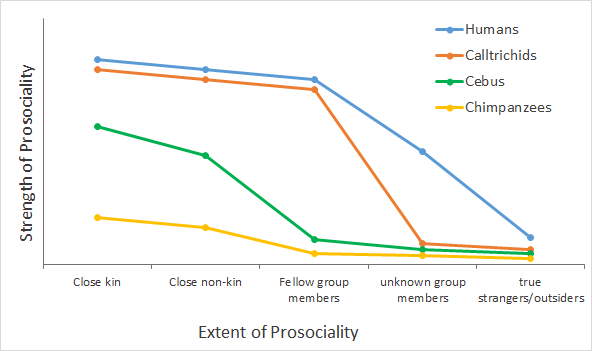
For biologists, prosociality refers to behaviors that benefit others. Spontaneous prosociality is the ability and motivation to be friendly, to tolerate others’ presence, or to share things and information with others, without “threat” or “rational calculation,” but rather spontaneously or voluntarily. Spontaneous prosociality is thus not tied to “intelligence” or certain cognitive abilities, but to a particular social temperament. When biologists compare the extent of prosociality in different animal species, they find that those species that live in groups and collaboratively raise their offspring, have a pronounced prosocial temperament. Apparently, a prosocial temperament has an important function in sustaining groups in which everyone is “in the same boat”.
It appears that humans have a particularly strong prosocial motivation compared to other primates, even towards unknown others. Some anthropologists call this trait “Ultrasociality”.
This association into ever larger groups was made possible in our species by the ability for language and symbolic thinking. This ability allowed our ancestors to build a common identity and cooperate with others, even if they would never meet them in person.
So on the one hand, the history of humanity is characterized by conflict between groups, but on the other hand, in the long run this resulted in the joining of groups of people into ever larger communities as we recognized and acted on our social interdependencies. The fact that today many people of different backgrounds live together, and work together for global goals, universal human rights and the well-being of humans and other creatures they will never encounter, is the result of this development.

“The capacity for symbolic thinking was the last great evolutionary innovation that made possible human ultrasociality. People now did not need to know personally another individual in order to determine whether to cooperate with him, or treat him as an enemy. (...) Symbolic demarcation of the group made possible cooperating with strangers who were clearly marked as “one of us.” Symbols made it possible to identify with very large groups of “us,” groups that included many more people than the small circle any individual person could meet and get to know personally. In other words, the evolution of symbolic thinking enabled defining as “us” a group of any size.”
“Large nations of tens of millions of people did not, of course, arise in one fell swoop. The process was gradual and happened in stages. Several villages, threatened by a powerful enemy, could unite in a tribe and invent symbolic ways to mark and emphasize their union. In the next stage, several tribes could unite in a region-sized society; then regional societies into nations, and those, finally into supranational unions, such as large empires and whole civilizations. At each step, new symbols are invented to demarcate ethnic boundaries, or old symbols are stretched to encompass the larger society.”
“As a new level of social complexity arose, the lower levels of organization were not completely eroded. As a result, people in general have coexisting identities, nested within each other. They can feel attachment and loyalty to their native town, their region, their country, and even to supranational organizations. The degree of identification with, and loyalty felt toward, an identity at any particular level can vary a lot.“
Peter Turchin (2006)
The historian Yuval Harari talks about the importance of symbolic thinking and language in the extraordinary cooperation in our species.
Possible reflection questions:
- According to Yuval Harari, what distinguishes human forms of cooperation from cooperation in other animal species?
- What kinds of groups are there in your school, in your community, in your country? What role do symbols and our ability for symbolic thinking play in these groupings and in the identity of their members? Are there flags, crests, slogans, certain clothing styles, music groups, stickers, tags or other symbols that characterize the members of these groups?
- Do these symbols also affect the behavior of group members towards other groups? In what way?
Causal map: Cooperation between groups
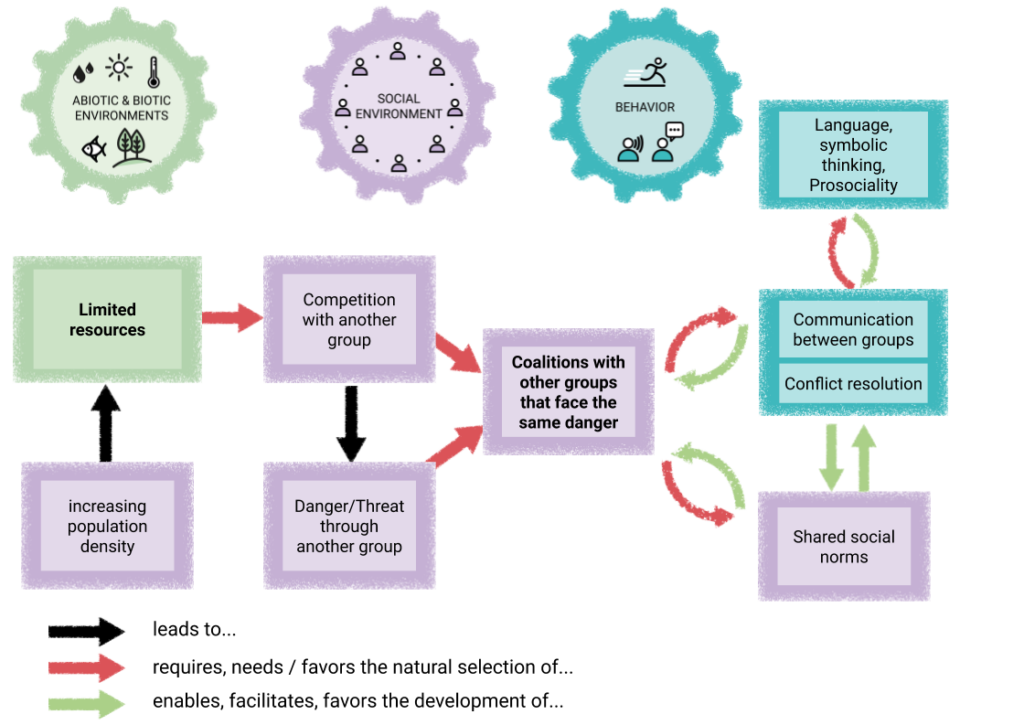
On the other hand, if resources were limited (e.g., due to population growth), competition between groups increased, and thus the danger emanating from other groups increased.
Under these conditions, those who had the opportunity to band together with other groups facing the same threat were at an advantage.
Causal maps on the evolution of human traits
All causal maps on human evolution in one Google slide file
Ethnocentrism
However, due to the history of group competition, we humans also have a tendency to quickly and automatically divide our social environment into groups – “we” and “the others”. We automatically and relatively unconsciously recognize similarities and differences in our behavior, appearance, language, beliefs and symbolic markings. Under certain conditions, especially when there is a perception that the others are posing a “danger” or “threat”, this perception may encourage aggression towards other groups.
Thus, the history of our species shows us that our ability to work together peacefully with fellow humans is not unconditional.
Our sense of who belongs to “us”, and what attitudes and relationships we have with other groups, seems highly flexible and changeable. Groups plagued by violent clashes for centuries now live together peacefully and cooperate for common benefit. Groups who lived together peacefully for centuries suddenly start fighting each other violently.
What conditions and mechanisms lead to these different perceptions and behaviors towards other groups? Anthropologists and behavioral researchers examine these questions. For example, already in infancy we seem to prefer those who resemble us. In experiments, people seem to prefer members of “their group”, even if the distinction is sometimes quite arbitrary and one does not even know one another.
But hostility or aggression towards those who are less like us or who belong to the “other group” does not necessarily arise from this. Apparently it depends on whether the “other group” is perceived as danger or competition. Are we all in the same boat – and are we all in this together? Or are we sitting in different boats, and “Their Victory” is “Our Defeat”?
Ethnocentrism stands for the conviction that the “own group” and its behaviors and norms are “good”, “right”, “justified” and “normal”, and those of other groups “bad”, “wrong”, “irrational” and are “abnormal”.
Ethnocentrism has many faces – racism, anti-semitism, or any ideological more or less radical movement that identifies a particular group of people as the cause of perceived problems.
Possible reflection questions:
- What factors (other than limited natural resources) could have contributed throughout history to groups competing with one another or engaging in aggression?
- What events in history or the present can you think of, in which competition between groups and / or ethnocentrism play(ed) a role?
- How could we represent these historical or current events in a causal diagram?
- How does ethnocentrism affect the sustainable development of our societies?
- What can we do to prevent or reduce the negative consequences of ethnocentric tendencies?
see also:
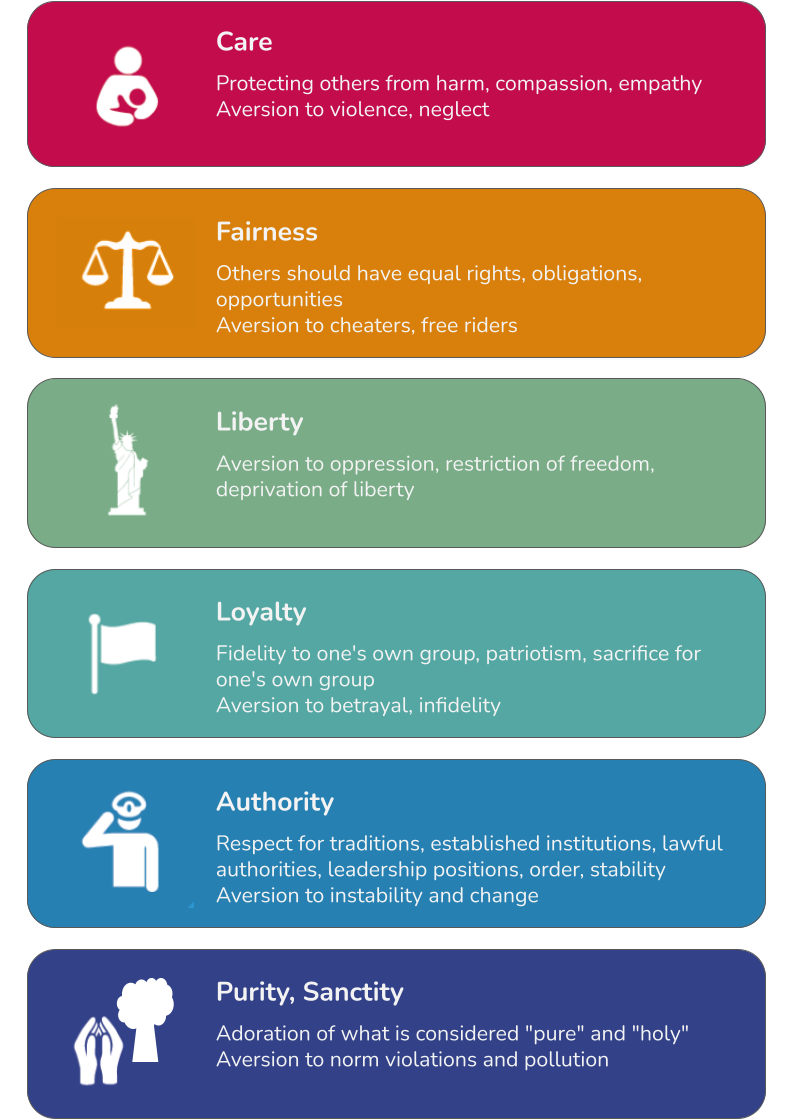
Noticing moral intuitions
Students identify the moral intuitions underlying people’s opinions in quoted texts and images.

True stories of people who left radical movements
In this unit students explore stories of people who have left a radical movement, or deliberately discuss with representatives of the “other side” and build respectful relationships. These let us explore the circumstances, experiences and insights about why prejudice, hatred and violence against other people or a group can arise and how they can dissolve again.
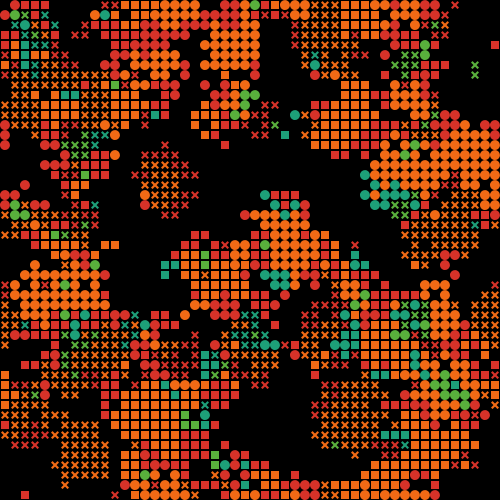
NetLogo: Evolution of ethnocentrism
This model simulates the biological evolution of ethnocentrism in a population made up of multiple ethnicities.
References
- Brooks, A. S., Brooks, A. S., Yellen, J. E., Potts, R., Behrensmeyer, A. K., Deino, A. L., … Clark, J. B. (2018). Long-distance stone transport and pigment use in the earliest Middle Stone Age. Science, 2646(March), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao2646
- Burkart, J. M., Hrdy, S. B., & van Schaik, C. P. (2009). Cooperative Breeding and Human Cognitive Evolution. Evolutionary Anthropology, 18, 175–186. https://doi.org/10.1002/evan.20222
- Hamlin, J. K., Mahajan, N., Liberman, Z., & Wynn, K. (2013). Not like me = bad: Infants prefer those who harm dissimilar others. Psych. Sci., 24(4), 589–594. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797612457785
- Mahajan, N., & Wynn, K. (2012). Origins of “Us” versus “Them”: Prelinguistic infants prefer similar others. Cognition, 124(2), 227–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2012.05.003
- Pisor, A. C., & Surbeck, M. (2019). The evolution of intergroup tolerance in nonhuman primates and humans. Evolutionary Anthropology: Issues, News, and Reviews, 28(4), 210–223. https://doi.org/10.1002/evan.21793
- Turchin, P. (2006). War and Peace and War. The rise and fall of empires. New York, NY, USA: Penguin.

